The Countdown to Collapse and the Demographic Doomsday: 10 Countries With Declining Populations
The global population curve inversion (when it stops growing and starts to decrease) is a moment that is apparently coming faster than experts expected decades ago, and there are multiple countries with declining populations already. In some of them, problems are getting serious.
Recent reports predict the global population will peak at 9.7 billion in 2064 before declining.
But way before that, multiple countries will see their populations decrease to the point of collapsing structures like workforce and (most of all), social security.
See also: Your Retirement is an Illusion: Why Most of Us Will Work to Death
It is a ticking time bomb for numerous nations across the globe (while it will also benefit immensely some people).
Some nations may face such drastic drops in the numbers of their young, tax-paying citizens that the funding of their government structures may be wiped out due to lacking budgets.
There are many reasons to blame (or thank for, if you are one of those that benefit from shrinking populations) for the demographic collapse in these countries. This is a phenomenon that has been attributed to things like increased birth control, family planning, urbanization, increasing costs, and changing cultural norms.
The problems caused by population decline are not very visible when we talk about marginal percentages, like a 2 or 3% decline in a time span of decades.

But in the next few paragraphs, we will show you countries that may lose up to one-quarter of their total population in a matter of decades.
This doesn’t happen without some nasty consequences.
That means ghost cities, economic downfall, collapsed social security, and obliteration of tax revenues in many countries.

The Criteria Used to Determine the Worst Ten Countries With Declining Populations
First of all, the 10 countries below are not the absolute worst regarding forecasted population decline. There are nations like Latvia or some islands in the Pacific Ocean that have even worse demographic decreases but didn’t make it to the list because they are too small.
That is because we only considered countries with more than 5 million residents.
Another filter applied was to take out countries that are currently experiencing a considerable inflow or outflow of refugees. For example, both Poland and Ukraine experienced enormous population changes last year due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
While Poland gained millions of new residents, Ukraine lost a considerable share. But this is likely not a permanent demographic change and often refugees return to their countries after armed conflicts. That is the reason we didn’t consider demographic challenges in both countries (although they do exist).
The Data Source
All the information about past populations and the forecasted number of residents in the countries mentioned below is from the 2022 data release from the UN Population Division.
Some additional information is from OurWorldInData. Data about fertility rates are from UNFPA or from the World Bank.
All the population pyramids are from populationpyramid.net.
Other sources (like the provided demographic pyramids) are linked after their respective mentions.
What a “healthy” demographic pyramid looks like
One of the few countries in Europe that are close to the population replacement fertility rate (2.1 children per woman) is Azerbaijan (although one could argue that they are actually located in Asia).
Their population pyramid looks like this:
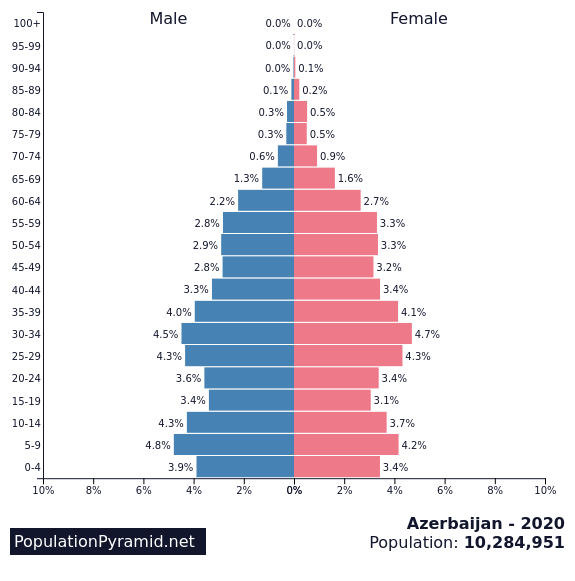
A country with a stable population usually has a population pyramid with roughly the same number of people in each age and gender group.
The pyramid has a somewhat rectangular shape with relatively equal numbers of people in each age range, with a slightly wider base representing the younger age groups and a slightly narrower top representing the older age groups. The number of men and women is about the same.
What the demographic pyramid of a fast-growing country looks like
The fastest-growing country in the world (in terms of population) is Niger. Their birth rate is a whopping 6.6 children per woman. Below is their population pyramid.
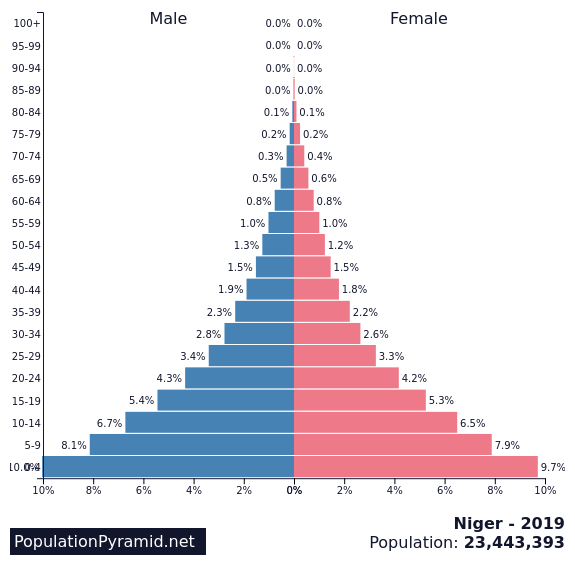
The pyramid of a country like Niger, with a rapidly growing population, has a wide base and a narrow top, indicating a high proportion of young people.
Now that you know what the population pyramids of stable and growing countries look like, time to jump into the countries with declining populations.
Low Fertility Rates – What It Means
The fertility rate is a measure of the average number of children born to a woman over her lifetime, in a specific population or region.
It is calculated by dividing the total number of live births in a given year by the number of women of reproductive age (usually defined as ages 15-49) in that same year and then multiplying the result by a factor that adjusts for the age distribution of women in the population.
The replacement fertility rate is the number of children that each woman needs to have on average in order to replace herself and her partner in the population over the long term.
In other words, it is the fertility rate at which the population size remains constant, neither increasing nor decreasing.
The replacement fertility rate is typically estimated to be around 2.1 children per woman.
Any country with a fertility rate lower than that tends to have a population decline unless it increases life expectancy or experiences an inflow of immigrants.
Read also: The 5 Fastest Growing Cities in Europe Have Some Curious Things in Common

The Fastest-Shrinking Countries in the World: Declining Populations
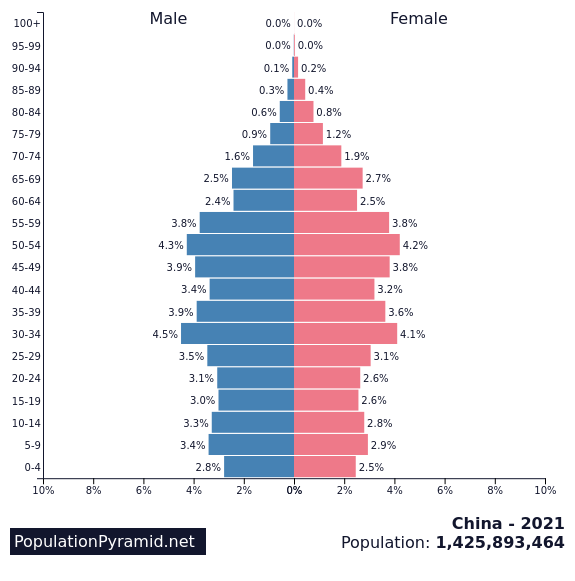
10th – China
Fertility rate: 1.45 births per woman
Population in 1990: 1,153,704,200 people
Population in 2022: 1,425,887,400 people
Projected Population for 2050: 1,312,636,300 people
Forecasted population decline of China: -7.9%
One of the main reasons for the Chinese decline is the country’s one-child policy, which was in place from 1979 to 2015.
The policy was meant to control the population growth rate, but it had unintended consequences, such as a disproportionately high number of male children being born due to a cultural preference for sons. China is the worldwide leader in the number of abortions already for decades, and abortive procedures often are executed after parents discovering they will have a girl.
The policy has also led to an aging population and a shrinking workforce, which could have a negative impact on China’s economic and growth rate. Additionally, the high cost of living in urban areas has discouraged people from having children, and many couples are choosing to delay or forgo having children altogether.
Another contributing factor is China’s rapidly aging population, which puts pressure on the country’s healthcare and pension systems.
The country’s birth rate has been consistently declining since the 1980s, and as a result, the proportion of elderly people is increasing. By 2050, it is estimated that almost 30% of the Chinese population will be over 60 years old. This aging population puts pressure on the government to provide adequate healthcare and pension benefits, while also raising concerns about the future of the country’s workforce and economic growth.
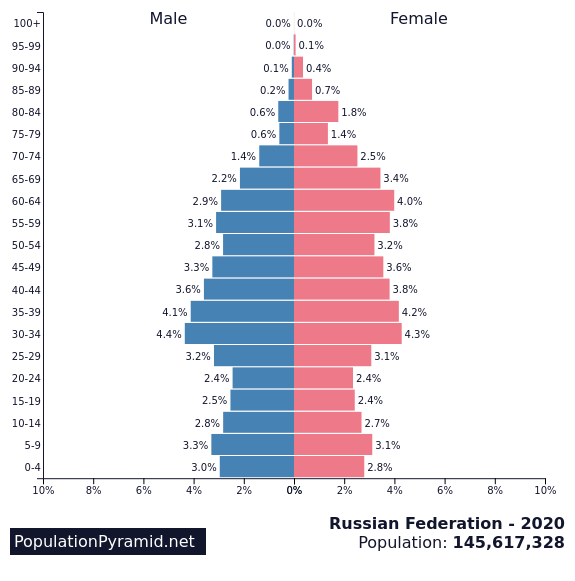
9th – Russia
Fertility rate: 1.5 births per woman
Population in 1990: 148,005,700
Population in 2022: 144,713,310
Projected Population for 2050: 133,133,030
Forecasted population decline of Russia: -8%
Russia’s population decline is due to a combination of low fertility rates, high mortality rates, and emigration.
Emigration is a major problem both in the poorest areas since Russia is one of the most unequal countries in the world, but also in large urban and richer areas, where educated Russians leave the country in a massive brain drain, since they prefer to work abroad for bigger salaries.
According to the United Nations, Russia’s population is expected to decline by 10 million people by 2050. Factors contributing to this decline include high levels of alcohol and tobacco consumption, a lack of access to quality healthcare, and a high incidence of infectious diseases.
Emigration is also a significant factor, with many young and educated Russians leaving the country in search of better opportunities, something that increased after the sanctions imposed due to the invasion of Ukraine. Western countries and even places in the middle east like Dubai received considerable number of Russians escaping sanctions.
One curious phenomenon in Russia is that male life expectancy is way lower than female due to high suicide rates, violence, and alcoholism.
8th – Portugal
Fertility rate: 1.44 births per woman
Population in 1990: 10,007,347
Population in 2022: 10,270,857
Projected Population for 2050: 9,261,306
Forecasted population decline of Portugal: -9.8%
Portugal’s population decline is due to low fertility rates and emigration (despite it being very attractive to foreign pensioners and figuring among the best retirement destinations in the world). It managed to keep it population somehow stable during the last decades due to an influx of immigrants from Brazil and other portuguese speaking nations, as well as expatriates looking to retire with high standards of life while spending little.
According to a report by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Portugal has the highest rate of emigration among OECD countries, with an estimated 2.5 million Portuguese citizens living abroad.
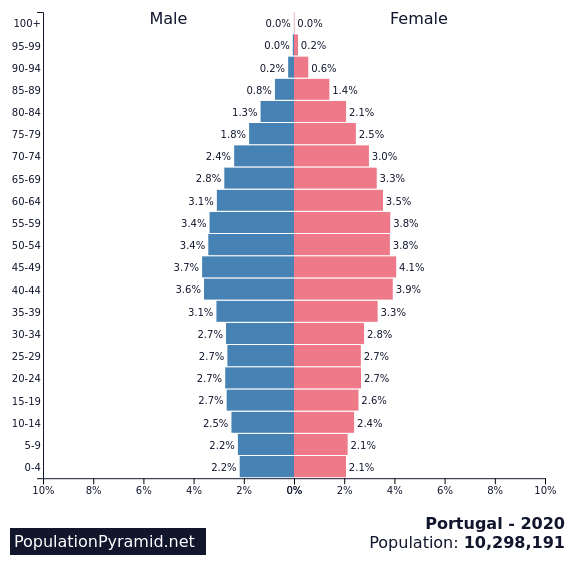
7th – Cuba
Fertility rate: 1.6 births per woman
Population in 1990: 10,626,679
Population in 2022: 11,212,198
Projected Population for 2050: 10,028,082
Forecasted population decline of Cuba: -10.6%
In Cuba, the demographic decline is due to low birth rates and emigration. Cuba’s birth rate has been declining since the 1970s, due in part to family planning policies, economic pressure and changing cultural norms.
Emigration, especially from the Island to the USA, has also been a factor.
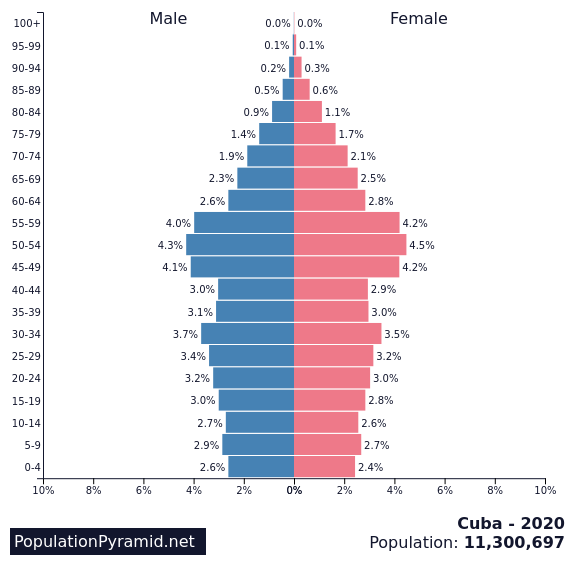
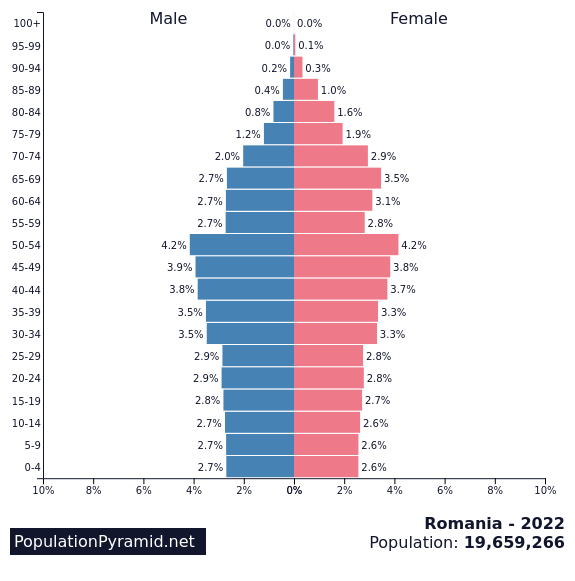
6th – Romania
Fertility rate: 1.58 births per woman
Population in 1990: 22,836,234
Population in 2022: 19,659,270
Projected Population for 2050: 17,457,214
Forecasted population decline of Romania: -11.2%
Romania’s declining population is due to low fertility rates and emigration in recent years. Many young and educated Romanians left the country in search of better opportunities.
This is a common situation in Eastern Europe, and that is why there is one of the neighboring countries of Romania at the top of this list.
According to a report from Bloomberg, during the past decade, millions of Romanians have left the country and headed toward more developed countries since their admission into the European Union
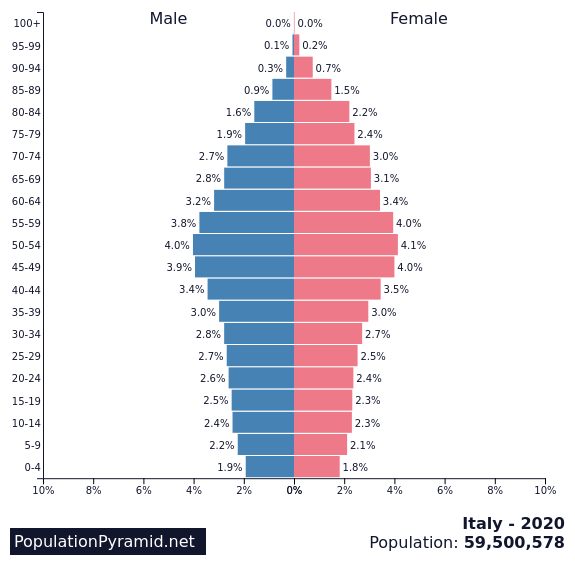
5th – Italy
Fertility rate: 1.3 births per woman
Population in 1990: 56,756,560
Population in 2022: 59,037,470
Projected Population for 2050: 52,250,484
Forecasted population decline of Italy: -11.5%
Italy’s population decline is due to low fertility rates and aging. The country has one of the lowest birth rates outside eastern Asia, with an average of 1.3 children per woman.
Italy also has one of the oldest populations in the world, with a median age of 47.3 years. This demographic shift is putting a strain on the country’s economy and social welfare systems, as there are fewer young people to support the growing number of elderly citizens.
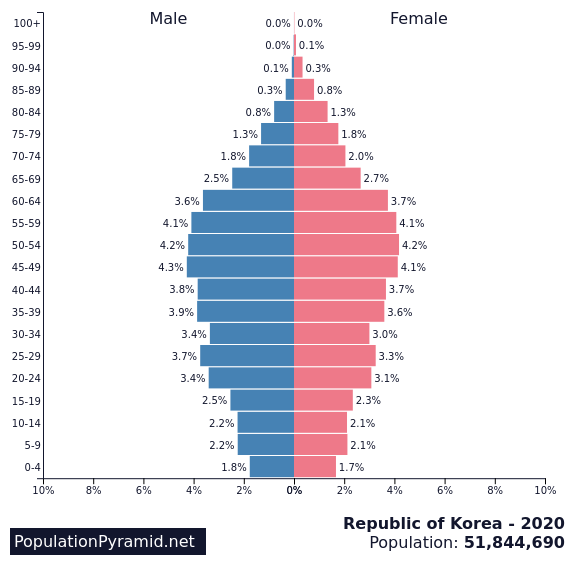
4th – South Korea
Fertility rate: 1.39 births per woman
Population in 1990: 44,120,040
Population in 2022: 51,815,810
Projected Population for 2050: 45,770,870
Forecasted population decline of South Korea: -11.7%
In South Korea, the demographic decline is driven by low birth rates and an aging population. South Korea has one of the lowest birth rates in the world, due in part to changing cultural norms and economic pressures.
One of the main reasons for such low numbers is the fact that the country has one of the worst work-life balances in the world according to the OECD.
The country also has a rapidly aging and declining population now, with a growing number of elderly people who require care and support.
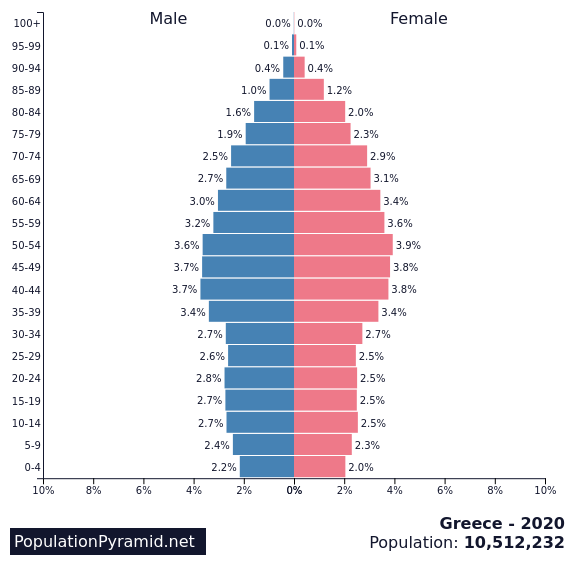
3th – Greece
Fertility rate: 1.31 births per woman
Population in 1990: 10,302,255
Population in 2022: 10,384,972
Projected Population for 2050: 9,144,953
Forecasted population decline of Greece: -11.9%
Greece’s population is expected to drop almost 12% during the next decades, and the demographic decline is due to a combination of lower birth rates (an issue common in many european countries), high emigration, and an aging population.
Greece’s birth rate has been declining since the 1980s, and emigration has been a factor as young people leave in search of better economic opportunities and to escape the negative impacts of the serious economic downfall that started in 2009.
The country’s population also has a high proportion of elderly people, with a low ratio of working-age people to support them.
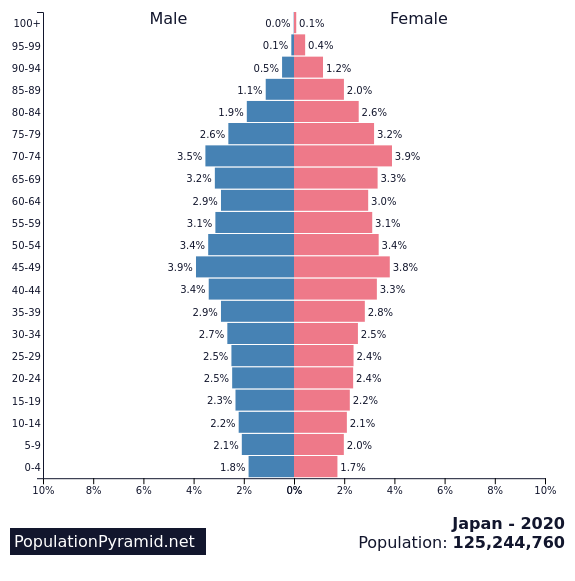
2th – Japan
Fertility rate: 1.34
Population in 1990: 123,686,320
Population in 2022: 123,951,700
Projected Population for 2050: 103,784,360
Forecasted population decline of Japan: -16.3%
In Japan, the demographic decline is largely due to a low birth rate and an aging population. Japan has one of the lowest birth rates in the world, due in part to changing cultural norms and economic pressures.
The country also has a rapidly aging population, with a growing number of elderly people who require care and support. Japan’s government has been implementing policies to encourage people to have more children, such as increasing childcare support and offering financial incentives.
However, these policies have had limited success so far in reversing the country’s demographic decline.
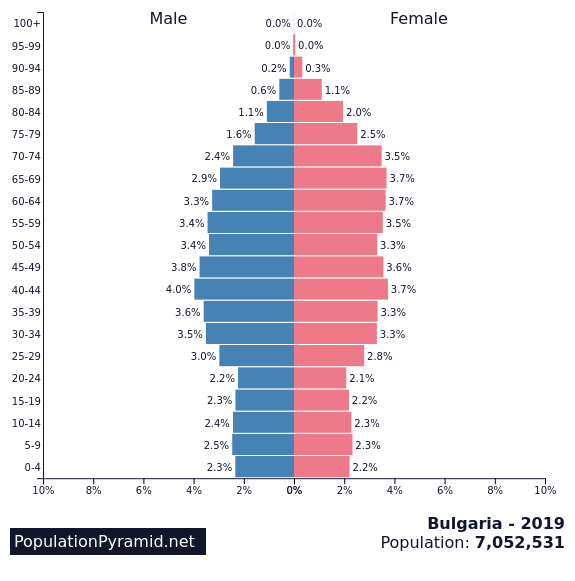
1st – Bulgaria
Fertility rate: 1.56
Population in 1990: 8,767,778
Population in 2022: 6,781,955
Projected Population for 2050: 5,187,394
Forecasted population decline of Bulgaria: -23.5%
Bulgaria tops our list of countries with declining populations, but as we can see, their fertility rateis not that bad when compared to other countries in this list (although still alarmingly below replacement levels). That gives a hint that the reason for Bulgaria occupying the top place among the fastest declining populations is another.
It is an issue that also affected a few other Eastern European countries: the exodus of young professionals after the entrance into the European Union. The population decline may be well one of the reasons the local government instituted programs to bring remote workers and pensioners to Bulgaria.
After Bulgaria’s entrance into the European Union in 2007, many Bulgarians emigrated to other EU countries in search of better economic opportunities and higher standards of living. This resulted in a brain drain of skilled workers, leaving behind an aging population with fewer young people to support them.
So, Tl;DR: Bulgaria’s demographic decline is due to a combination of factors, including low birth rates, high death rates, and, most of all, emigration. Curiously, despite the low fertility rates, Bulgaria is also one of the easiest countries in the world to adopt a baby from.
What More We Should Know About The Current Population Decline?
What is the main reason behind the current population decline in many countries?
The main reasons behind the declining population in many countries, particularly in European countries, are a combination of low fertility rates, aging population, and high emigration rates. The fertility rate in these countries has significantly dropped below the replacement level of 2.1 births per woman, leading to fewer births and an overall population decline. Furthermore, the aging population results in a higher death rate, and high emigration rates cause a loss of young working-age individuals, further contributing to the problem.
What is the global impact of an expected population decline?
The global population is expected to reach its peak around 2100 and then start to decline slowly. This could have several implications such as economic challenges due to a shrinking workforce and the increasing costs of providing healthcare and social services to an aging population. Furthermore, a declining population can lead to reduced demand for goods and services, lower economic growth, and potential political instability in affected countries.
If you enjoyed this article about countries with declining populations, here are a few other reading suggestions for you:
The Best Cities for Remote Workers in 2023
The Mind-Blowing Tourist Scams You Can Find in Europe
Subscribe (for free) to receive my articles directly in your inbox and receive a special gift. If you enjoy this article, please consider becoming a Medium member by using this link and have access to premium, unbiased content from authors not tied to big media.
Levi Borba is the founder of The Expatriate Consultancy, creator of the channel The Expat, and best-selling author. Some of the links in this article may be affiliate links, meaning that the author will have a commission for any transactions.




